Are there any regulatory or compliance requirements for the installation of automatic door infrared sensors?
Automatic door infrared sensors have become ubiquitous in public and commercial spaces, providing convenience and safety by detecting the presence of individuals and activating door opening mechanisms. However, to ensure the safe and reliable operation of these sensors, there are regulatory and compliance requirements that must be adhered to during installation. In this article, we will explore the essential regulations and standards governing the installation of automatic door infrared sensors.
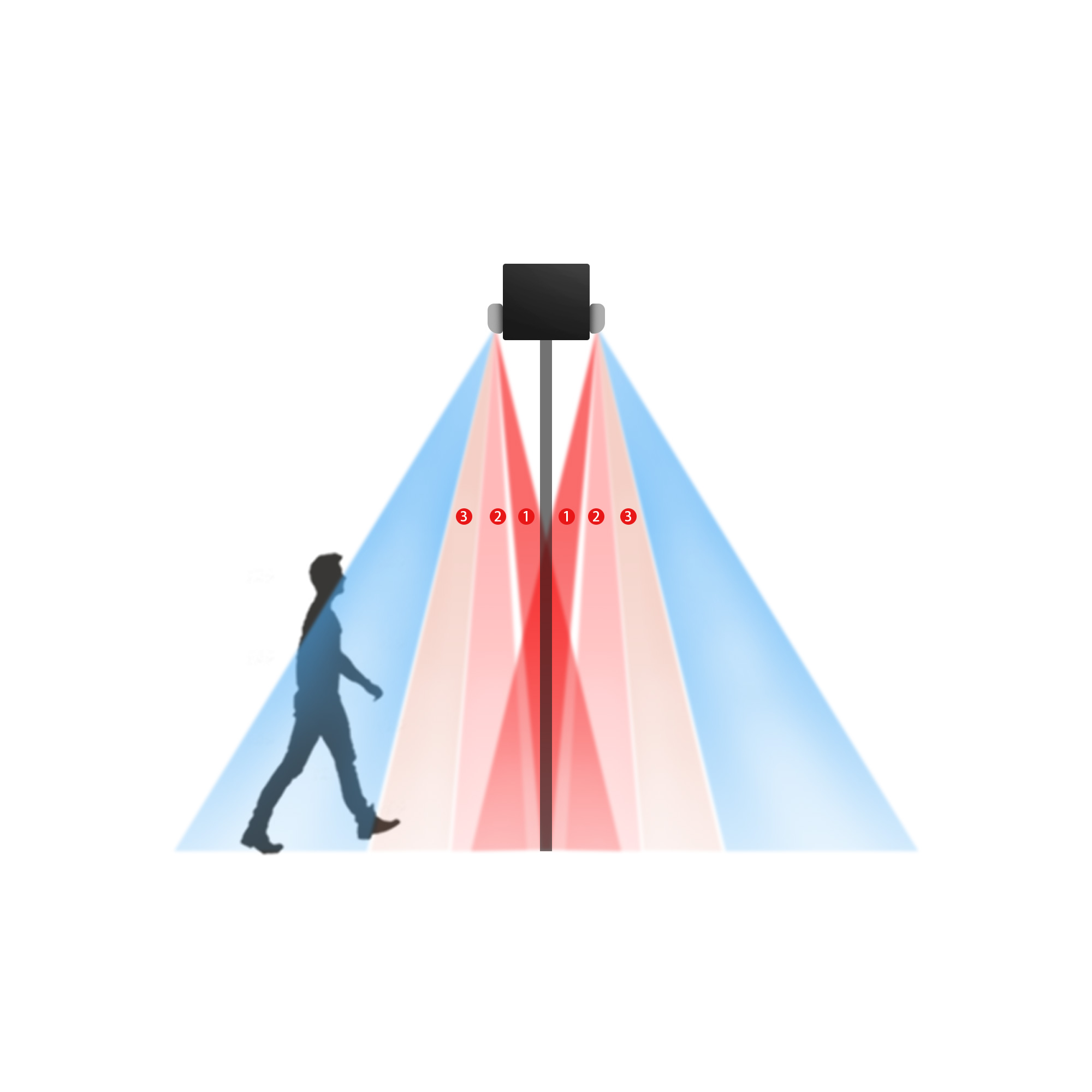
1. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
The Americans with Disabilities Act sets specific requirements for accessible entrances, which often include automatic doors with infrared sensors. To comply with ADA, sensors must be installed at the correct height and distance from the door to ensure accessibility for individuals with disabilities. Additionally, the sensors must have appropriate activation time delays to accommodate individuals entering or exiting.
2. National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
NFPA 101, the Life Safety Code, addresses the installation of automatic doors, including infrared sensors, in areas of egress. These regulations ensure that automatic doors equipped with sensors do not impede emergency evacuations and provide safe passage during fire emergencies. Compliance involves the appropriate installation, signage, and backup power requirements for these systems.
3. International Building Code (IBC)
The International Building Code outlines safety and accessibility requirements for buildings and their components, including automatic doors. It stipulates that automatic doors, when equipped with infrared sensors, should be designed and installed to accommodate individuals with disabilities and ensure safe operation during normal and emergency conditions.
4. Underwriters Laboratories (UL)
UL provides safety standards for various electrical and electronic products. Automatic door infrared sensors should comply with UL standards to ensure their electrical safety and reliability. Installers should confirm that the sensors they use are UL-listed or UL-certified.
5. ANSI/BHMA Standards
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association (BHMA) have developed standards specifically for automatic door sensors. ANSI/BHMA standards cover topics such as sensor testing, durability, and environmental conditions to ensure proper sensor operation over time.
6. Local Building Codes
In addition to national and international standards, local building codes may include specific requirements for the installation of automatic door infrared sensors. It's essential to consult local building authorities to ensure compliance with regional regulations.
7. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
OSHA regulations may apply to the installation process, particularly for commercial or industrial settings. Installers must follow OSHA safety guidelines during the installation of sensors and related equipment.
8. Manufacturer's Recommendations
Manufacturers typically provide installation guidelines and recommendations for their specific infrared sensor products. It is crucial to follow these instructions to maintain the warranty and ensure the sensors' proper function.
Conclusion
Automatic door infrared sensors are critical components of modern building access systems, providing convenience and accessibility. To ensure the safety and compliance of these systems, installers and building owners must adhere to various regulatory and compliance requirements, including ADA, NFPA, IBC, UL, ANSI/BHMA standards, local building codes, OSHA guidelines, and manufacturer recommendations. By following these standards, automatic door infrared sensors can enhance building accessibility while maintaining safety and compliance.







